- Escambia County Public Schools
- Biology End of Course Review
- SC.912.L.14.3 Cell Structure
Science
Page Navigation
- Home
- Elementary Science Curriculum
-
Biology End of Course Review
- Biology EOC Review
- SC.912.N.1.1 Scientific Method
- SC.912.L.18.12 Properties of Water
- SC.912.l.18.9 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
- SC.912.L.18.1 Macromolecules
- SC.912.L.16.17 Mitosis and Meiosis
- SC.912.L.16.3 DNA Replication
- SC.912.L.14.3 Cell Structure
- SC.912.L.14.1 Cell Theory
- SC.912.L.17.20 Human Impact
- SC.912.L.17.9 Food Webs and Energy Transfer
- SC.912.L.17.5 Population Size
- SC.912.L.16.13 Reproductive System
- SC.912.L.16.10 Biotechnology
- SC.912.L.14.52 Immune System
- SC.912.L.14.36 Cardiovascular System
- SC.912.L.14.26 The Brain
- SC.912.L.14.7 Plant Structure
- SC.912.L.16.1 Genetics
- SC.912.L.15.13 Natural Selection
- SC.912.L.15.8 Origin of Life
- SC.912.l.15.6 Classification
- SC.912.L.15.1 Evolution
SC.912.L.14.3 Cell Structure
ORGANISMS, POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS
CLASSIFICATION, HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW...
-
- You need to know the general structures of plant and animal cells and how plant and animal cells are alike and different.
- You need to know the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and how they are alike and different.
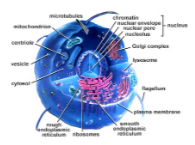
- You need to know how the structure relates to the function for the components of plant or animals cells. Structures you need to know are the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, plasmids, ribosomes, flagella, nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, chromatin, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, microtubules, microfilaments, vacuoles, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, lysosomes, and cilia
- You need to understand the role of the cell membrane as a highly selective barrier that carries out passive and active transport.
EXAMPLE ONE
-
There are some similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Which of the following structures is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. lysosome
B. mitochondrion
C. nucleus
D. ribosome
EXAMPLE TWO
-
Cells need to bring in molecules to carry out cellular processes. Often, this requires moving the molecules across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient. How do these molecules get into the cell?
A. passive transport by diffusion
B. active transport using ATP
C. passive transport by osmosis
D. phagocytosis
EXAMPLE THREE
-
Which type(s) of cells have genetic material that is contained in a nucleus?
A. bacteria
B. only animal cells
C. protists
D. both plant and animal cells
EXAMPLE FOUR
-
Which characteristic do most plants have in common?
A. they are unicellular
B. they are prokaryotic
C. they produce seeds
D. they are autotrophic
EXAMPLE FIVE
-
Which cell structure is correctly paired with its primary function?
A. ribosome - protein synthesis
B. mitochondrion - movement
C. vacuole - cell division
D. nucleus - storage of nutrients
EXAMPLE SIX
-
The diagram below represents a cell of a green plant.
Solar energy is used to produce energy-rich compounds in which structure?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
EXAMPLE SEVEN
-
A person with swollen gums rinses his mouth with warm salt water, and the swelling decreases. Which of the following has occurred?
A. The swollen gums have absorbed the saltwater solution.
B. The saltwater solution lowers the temperature of the water in the gums.
C. The salt in the solution has moved against the concentration gradient.
D. The water in the gums has moved out due to the high concentration of salt in the solution.
EXAMPLE EIGHT
-
The diagram below represents a cell.
Which organelle is the site where amino acids are synthesized into proteins?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
EXAMPLE NINE
-
Which of these best completes this concept map?
A. an animal cell
B. a prokaryotic cell
C. a virus
D. a plant cell
EXAMPLE TEN
-
The cell membrane of the red blood cell will allow water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide to pass through. Because other substances are blocked from entering, this membrane is called
A. perforated
B. semi-permeable
C. non-conductive
D. permeable
KHAN ACADEMY - PARTS OF A CELL
PLANT CELLS
ANIMAL CELLS
MEMBRANES & TRANSPORT
IN YOUR BOOK
-
General Biology - Sections 3.2 - 5.3, pg. 73 - 96
Honors Biology - Sections 7.2 - 7.4, pg. 160-189